When first learning about ADHD, it is often seen as a condition primarily affecting children, as its symptoms closely resemble typical childhood behaviors. However, if not addressed early, its effects can evolve into more serious psychological conditions. A deeper exploration of its nature, consequences, and both early and later effects reveals that ADHD can be far more disruptive than it initially appears.
Among neurodevelopmental disorders, ADHD is the most common mental health condition, particularly in children aged 4 to 12. It is typically diagnosed in children, and if not treated early, it can lead to more severe mental health issues as the child grows.
The possibilities of continuous failure in life due to ADHD are the same as in other mental health conditions like poor focus, anxiety disorder, depression etc. It is because people in this condition face lack of attentiveness, high impulsiveness and are tuned out most of the time. As a result, that person faces a lot of rejection by people around him or people he/she meets for the first time, leading to further challenges in personal and social interactions.
WHAT ARE DIFFERENT TYPES OF ADHD
According to experts, the likelihood of finding this condition in boys is higher than in girls. Symptoms of hyperactivity are more commonly observed in males. However, not being biased, signs of ADHD in girls may differ slightly from those in boys. There are primarily three types of ADHD:
Inattentive ADHD – Previously (before 1987) known as attention deficit disorder (ADD), is a type of ADHD that specifically affects an individual’s ability to maintain focus. Maintaining attention on tasks or work is not easy in this condition. Symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsiveness are less common in this type. Related symptoms.
- Showing negligence in completing tasks. As a result, making silly mistakes.
- Finding it hard to finish tasks that require sustained attention.
- Gets distracted very easily by external stimuli.
- Avoiding tasks that seem uninteresting or boring.
- Not showing proper attention when someone calls or speaks.
- Forgets things easily even if they are in use regularly.
- Finding it hard to organize things.
The likelihood of being poor at studies is higher for a child with inattentive ADHD.

Hyperactive/Impulsive – In this type of ADHD, child shows signs of hyperactivity and impulsiveness when performing daily tasks. Signs of inattentiveness are fewer in this disorder. Although the child focuses on tasks, instructions and what is being told but they start answering, interrupting, reacting or moving before expected. Common symptoms are –
- Being impatient all the time.
- The energy level is exceptionally high most of the time of the day.
- Try to break in every time before someone has finished talking. Talks a lot.
- Continuous body movement can be noticed, like moving hands, legs (fidgeting).
- Cannot sit still when compulsory, like in the classroom.
- Has difficulty waiting for their turn.
- That child/person generally does not think before acting.
- Often interrupts others while they are working, driving, or eating.
Combined – It is the most prevalent one among all ADHD types. Mostly, those who have ADHD have combined symptoms. According to experts, one must show at least six symptoms of both inattentive and hyperactive in order to be diagnosed with ADHD. This form is often considered the classical presentation of ADHD.
Some of these symptoms can also be observed in children without ADHD. If a child exhibits some of these signs but performs well in daily tasks, it is advisable to consult a specialist for a proper diagnosis. The severity of the condition depends on how it impacts the individual’s daily life.
IN CHILDREN VS ADULTS
Children are generally more sensitive and vulnerable than adults. Taking care of our child’s mental health is essential. If a child faces issues like these during critical stages of development, it can significantly hinder their learning process. In the long run, this may make them less competitive in a world full of challenges.
Some children with ADHD symptoms (also in case of other mental health issues) may display arrogant or rude behavior when asked to perform daily chores, homework, or similar tasks. These children often fail to pay attention to instructions from parents and teachers, which might be annoying. But the reason behind such a reaction from a child could be their resentment and frustration.
In many cases, neither the children nor the people around them get a clue of what is really going on. Most of the time, even when that child or person is serious and diligent in doing something, they still experience failure. This increases their anxiety and lowers their self-esteem. Over time, as a response to frustration and anxiety, children may begin to feel more secure by reacting to such situations with aggression.
To diagnose ADHD in an adult, symptoms must have been present since age 12 or earlier. If not diagnosed and treated during childhood, ADHD can become more severe in adulthood. Symptoms could change into more serious issues.
It can lead to emotional instability, depression, social anxiety, a sense of lifelessness, and concentration difficulties. As we grow older, responsibilities also increase, but a person who has been facing challenges since childhood may struggle with managing responsibilities.
In adulthood, inattentiveness may develop into difficulties with maintaining focus. It becomes common to quickly lose interest in work, surroundings, and people. Owing to the problem of maintaining focus for long, decision-making is also impaired.
Although hyperactivity may lessen over time, it often transforms into other issues like inner turmoil, difficulty remaining calm, and excessive talking (up to a level that annoys people around them).
While the transition of impulsivity into thoughtless behavior, irresponsible actions and careless spending can be noticed with time.
There is no exaggeration in saying most of the mind’s abilities are interconnected with each other. If one gets affected, others also have to face its reverberations.
CAUSES
No specific reasons have been confirmed yet, which identify the root cause of this condition. But according to experts, some of the causes behind it could be:
- Parental genetics play a significant role in a child’s mental health. Children whose parents had or have any mental health condition are more prone to developing ADHD and likewise disorders. It could be considered as the primary cause, as around 80% of the cases showed the role of parental genetics.

- Careless behavior at the time of pregnancy, for instance substance use such as drug abuse, smoking, or alcohol consumption, can cause brain changes in a developing child.
- Children with low birth weight or premature delivery are also more susceptible to brain changes.
- Brain injuries caused could also contribute to ADHD.
- However, lead exposure may also be a contributing factor, but it is very rare nowadays, especially in countries where lead use is restricted. Countries where lead use is still unregulated and have no strict child labor laws, cases of ADHD could be noticed.
CO-OCCURING CONDITIONS
- Social anxiety disorder – In this mental disorder, a child or person becomes fearful of public situations where they have to perform something in front of others, fearing judgement. It becomes difficult for the child to actively participate in groups or classes. Slowly and gradually the child becomes a fine example of an introvert.
- Depression –Repeatedly facing failure and not being able to do anything to correct the reasons behind, makes a child depressed after a certain point. If left undiagnosed, this can fill a child with fear of being inferior to other children (Inferiority Complex).
- Oppositional defiant disorder – It is a kind of behavioral disorder in which a child frequently refuses to cooperate with parents, teachers and other people around him. That child often shows absenteeism from work.
- Conduct disorder – A child showing extreme aggressive behavior, have a mischievous behavior of damaging public property and frequently manipulates others, then it could be a case of conduct disorder.
- Learning impairment – For a child with ADHD symptoms, learning new but complex topics could be a tall order. As a result, their academic performance at school may go down.
CURES
Behavior Management Training
Mostly these training programs include both children and parents. If needed, school teachers are also involved. Individual counseling for the child or parents, as well as group sessions involving both (parents and child) are conducted. In the case of a child or person with mild symptoms, this approach is taken as the primary and ideal treatment.
Social skills training
In this, children are taught skills to enhance their daily lives, including how to maintain peer relationships, build quality friendships, be stable. They learn important social skills such as fitting into groups, sharing, and helping others. Those children with high impulsivity, specific techniques are taught to help them stay calm, wait for their turn, taught to understand expressions, how to respond appropriately etc.
All in all, they are taught how to organize things in a better way. Development of reasoning skills in a child is very important part of their growth.
Helping children understand what they’re experiencing, what is really happening to them and explaining them it is not that big an issue that they might have made an impression in their mind, can make a significant positive impact. Teaching them to recognize the triggers and symptoms of hyperactivity and impulsiveness, makes them more vigilant about their condition. Also, helping them to cope with the changes after improvement is an essential part.
Parents training
Parents’ active involvement is crucial for improving the symptoms of ADHD. It involves understanding the behavior of a child with ADHD and learning how to adapt to their needs. Through study of many cases, it is observed that group sessions are more successful than individual sessions. Parental training can help reduce family tension. Stress management techniques play a vital role in soothing things out within the family.
Parents can join communities and support groups where they can connect with others who have children with ADHD or similar conditions to share their experiences. This surely reduces the parents’ frustration. After hearing people share their child’s improvement story and the struggle they had to go through reduces negativity and increases hope among parents.
A trustful environment should be established between parents and the child, giving assurance to them that they are not alone in this. They have their family understanding and supporting them.
SOME OTHER TIPS
Less distraction
The less the data, the less the mind wanders. So, instead of overwhelming the mind with unnecessary data from phones, laptops, or tablet screens, children should spend more time playing and interacting with their peers. Screen time should be limited and under the supervision of parents.
Staying healthy
A healthy mind is supported by a healthy body. Regular physical activity plus a healthy diet help stay physically fit. Encouraging a child to exercise regularly or letting him participate in any outdoor game, wholly or partially is also a wise way to focus their attention in one direction. And that direction could be achieving something like winning a medal. Avoiding processed and unhealthy food and switching to meals cooked at home can also have calming effects on human behavior.
Praising good behavior
It is seen that if we try to stop bad habits only by drawing a line but do not praise the wise habits alongside, bad things circulate more. Appreciating and rewarding a child for their good behavior encourages them to repeat it.
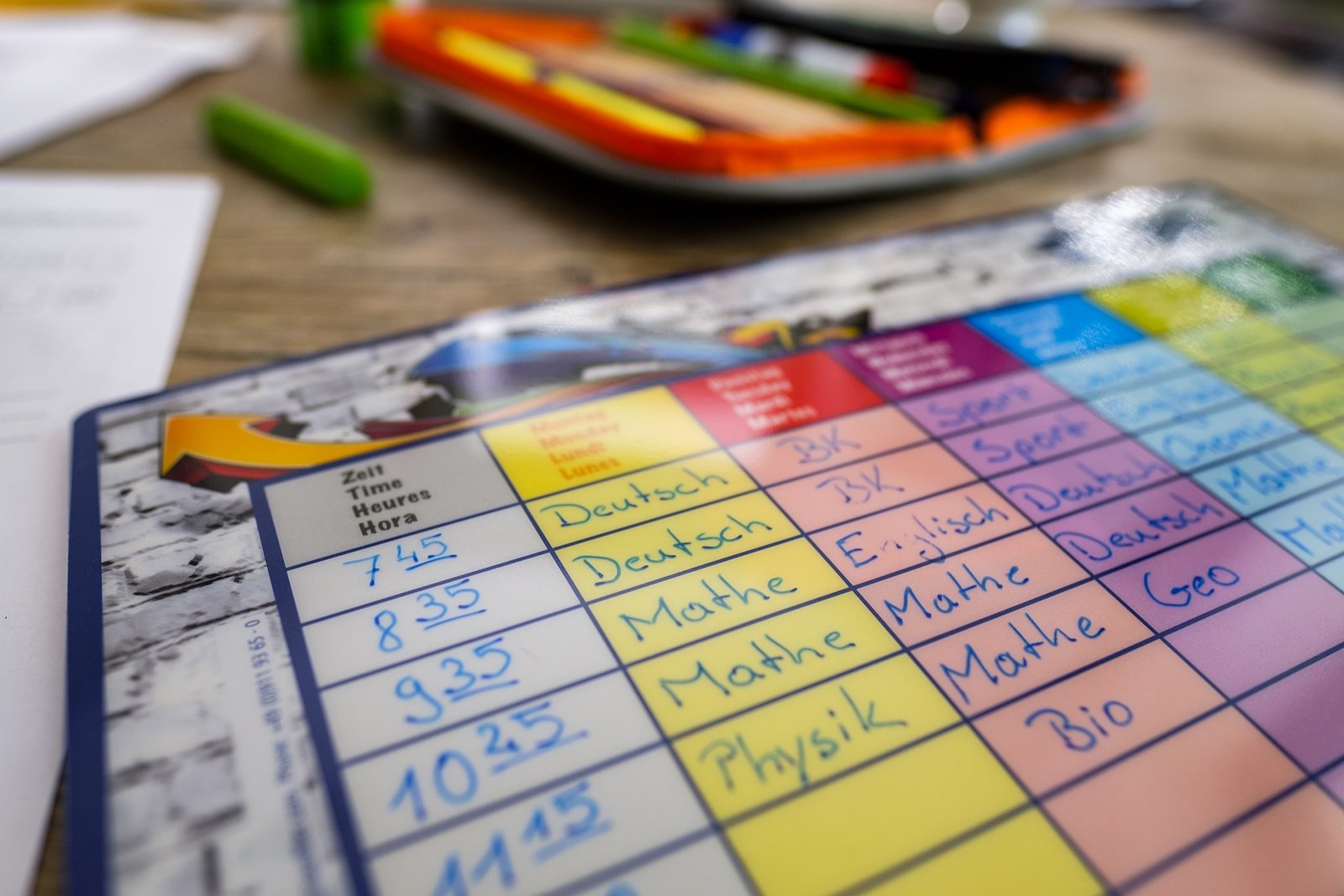
Time management/scheduling
Fixing a timetable for every chore and helping a child (showing ADHD symptoms) in maintaining that throughout the day prompts a feeling of independence and normality. It can uplift confidence and reduce the stress levels of a child.
Sleeping well
For the mind to perform well, it needs quality sleep. It improves the focus throughout the day and also helps in remembering and recalling different things and facts.
MEDICATION
It is considered better if the symptoms disappear without the use of pills. If not, then medication should be taken under the supervision of a qualified doctor.
The primary use of pills in curing ADHD is to boost the activity of two chemicals in the brain: norepinephrine and dopamine.
Norepinephrine hormones help the brain stay in alert mode. It makes us stay focused for longer, even if the task is outside our area of interest. Dopamine hormones motivate the mind to work on different tasks, and make the mind feel rewarded and happy about it. Together, these hormones make it easier to concentrate for longer periods and find enjoyment in completing tasks
Stimulants – Methylphenidate and amphetamine are main stimulants used to treat ADHD and other attention-related conditions. They give a fast response and are considered safe under supervision of a neuro physician or a psychiatrist.
Amphetamine is considered more effective than methylphenidate in case of teenagers. Whereas, when we want to use them for children, methylphenidate is typically considered as safe, effective and first-line treatment. Adderall, a commonly prescribed stimulant containing amphetamine salts, raises levels of norepinephrine and dopamine to help manage ADHD symptoms.
Non-stimulants – When stimulants do not work as expected then non-stimulants can be added to manage symptoms. Some people may have side effects on using stimulants; in that case non stimulants offer an effective alternative. Although they often take longer to work, non-stimulants can help increase focus and manage ADHD symptoms over time.
Experts advise having behavior therapy along with medication for the best results. If possible and has the right outcomes, behavioral therapy should be tried alone. Because medication could have addictive effects.
Risks
These medications can have adverse effects when used for long term or in an uncontrolled way. Norepinephrine hormone when in excess may disrupt the sleep cycle of a person, potentially leading to difficulty falling asleep or insomnia.
Dopamine could give rise to reward seeking behavior. Increased dopamine release in the brain could bring about the habit of procrastination. A person might not start working until they experience a dopamine boost. When this behavior becomes a habit, medication needs to be stopped immediately. On discontinuing the medication, relapse of symptoms is often observed in people. That is why, it is highly advised to use these medications under the supervision of a qualified healthcare provider.
CONCLUSION
Facing ADHD with maximum positivity is crucial at all points. There are chances of relapses of symptoms more than once, so being consistent is what is needed in every way possible. Negativity could arise within a family when no improvement is seen in the child, or on revert of symptoms. During these situations, parents must remain positive. A child’s determination to win over this condition is directly linked to their parents’ belief in them.





